About CTWWC Kenya
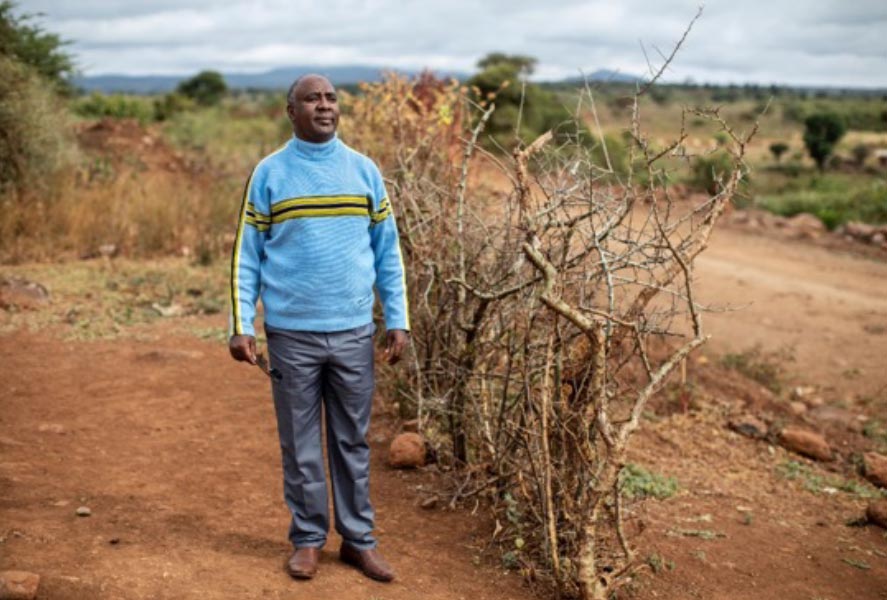
Changing the Way We Care℠ (CTWWC) Kenya began with a planning workshop in Nairobi, Kenya in October 2018. Working together with Kenya’s Ministry of Labor and Social Protection, which houses the Department of Children’s Services, The National Council for Children’s Services and the State Department of Social Development, the workshop participants identified three local counties and partners where they could demonstrate an alternative to residential child care (sometimes referred to as “orphanages” or “charitable children institutions”). Kisumu, Nyamira, Siaya and Kilifi Counties were selected because of their geographic diversity, standards of living, county government support, and engagement of local organizations and communities. In these counties, there are many reasons that children end up in residential care: poverty, HIV/AIDS, and the concentration of residential care institutions in urban areas which often attract families and children because of the resources they offer.
During the initial workshop, CTWWC Kenya also identified other programs in these three counties with which it could collaborate to create alternatives to child-family separation and promote family-based care for vulnerable children. These included CRS and Maestral programs, existing partnerships with local and national governments, UNICEF Kenya, and CRS’ existing partnership with Investing in Children and Their Societies, a local nonprofit organization working with children and families.
Want more information? Here’s a brief overview
Learn more about the situation for children separated from their families in Kenya and how CTWWC is ensuring that every child thrives in a safe and nurturing family.
About 40% of the population is under age 14
2.4 million children are orphans, 47% are AIDS orphans
Approximately 30-45% of these orphans end up in charitable children’s institutions (CCIs), sometimes referred to as “orphanages.”